In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations require infrastructure that balances reliability, high performance, and robust security. Enter the Cloud Dedicated Server—a solution that combines the flexibility of cloud computing with the power, control, and isolation of dedicated hardware. Unlike traditional shared hosting or virtualized environments, a cloud dedicated server provides exclusive physical resources to a single client, ensuring optimal performance and minimal disruptions. Key features include customizable hardware configurations, on-demand scalability, advanced networking options, and integrated security protocols designed for mission-critical workloads. With businesses increasingly relying on cloud-native applications, data analytics, and high-availability services, understanding the distinctions between cloud dedicated servers and conventional servers is essential. This overview explores how cloud dedicated servers are reshaping enterprise IT by delivering unparalleled performance, granular control, and superior resilience—empowering organizations to meet today’s complex business demands while planning for tomorrow’s innovations.
Overview of Cloud Dedicated Servers
Definition
A Cloud Dedicated Server is a form of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) that provides organizations with exclusive access to physical server resources, provisioned and managed through a cloud platform. Unlike traditional shared hosting or multi-tenant cloud environments, a cloud dedicated server allocates the entire hardware—including CPU, RAM, and storage—to a single client or workload. This ensures that resource contention is eliminated and performance remains consistent, even during peak usage. Cloud dedicated servers are typically deployed in state-of-the-art data centers and are accessible via secure, high-speed network connections. The provisioning, configuration, and management of these servers are streamlined through intuitive cloud control panels or APIs, allowing IT teams to rapidly deploy, scale, and manage infrastructure as business needs evolve.
Key Features
Cloud dedicated servers are engineered to meet the demanding needs of modern enterprises and mission-critical workloads. The following features distinguish them from both traditional dedicated servers and standard cloud instances:
– Exclusive Hardware Allocation: Clients receive access to the entire physical server, eliminating the resource variability and performance overhead associated with multi-tenant environments.
– On-Demand Scalability: Although each server is physically isolated, cloud orchestration enables rapid provisioning, deprovisioning, or resizing of resources, supporting dynamic business requirements and growth.
– Advanced Networking: Integrated with Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), software-defined networking (SDN), and dedicated IP addressing, these servers deliver enhanced network isolation, performance, and security.
– Enterprise-Grade Security: Features such as hardware firewalls, DDoS protection, encrypted storage, and compliance certifications (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS) are standard, making them suitable for regulated industries.
– Automation and Management Tools: Cloud APIs, Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools, automated backup solutions, and monitoring platforms enable streamlined operations and DevOps workflows.
– Disaster Recovery and High Availability: Integrated backup strategies, redundant network paths, and the ability to replicate workloads across multiple geographic regions enhance resilience and business continuity.
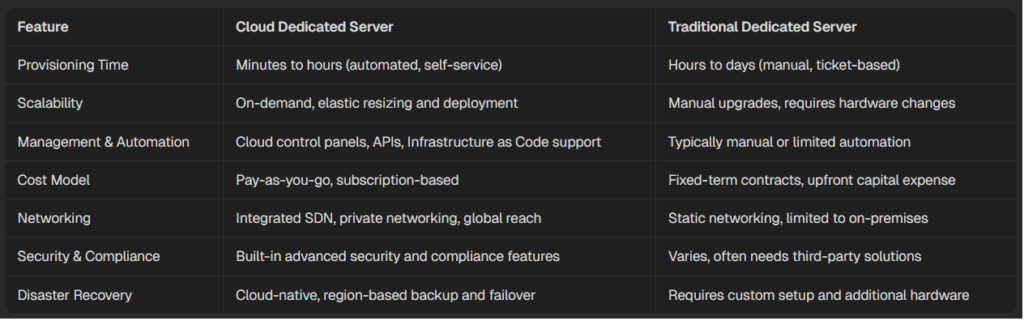
Comparison With Traditional Servers
Cloud dedicated servers and traditional dedicated servers both offer exclusive access to physical hardware, but key differences set them apart in terms of flexibility, management, and operational efficiency:
Cloud dedicated servers
In summary, cloud dedicated servers merge the raw power and isolation of traditional dedicated servers with the agility, automation, and cost efficiency of the cloud. As businesses navigate complex regulatory environments and require infrastructure that can adapt quickly to changing demands, cloud dedicated servers provide a strategic foundation for digital transformation, supporting both legacy workloads and modern, cloud-native applications.
Benefits and Use Cases of Cloud Dedicated Servers
Performance
One of the primary benefits of Cloud Dedicated Servers is consistent, high-performance computing. Because each server is dedicated to a single client, there is no resource contention with other users, which is often a concern in multitenant environments. The exclusive allocation of physical CPU cores, memory, and high-speed SSD storage results in predictable application performance, which is vital for mission-critical workloads. Many cloud providers also offer customizable hardware configurations, such as NVMe storage or high-frequency processors, to further optimize workloads for latency-sensitive tasks. Combined with advanced load balancing and network optimization, cloud dedicated servers ensure that applications and databases can handle high transaction volumes with minimal latency and downtime.
Scalability
Cloud Dedicated Servers blend the raw performance of bare-metal hardware with the agility and elasticity of the cloud. Unlike traditional dedicated infrastructure, which requires manual intervention for upgrades or expansions, cloud orchestration tools allow administrators to quickly provision new resources or scale existing ones to meet fluctuating demand. Vertical scaling (adding more resources to a server) and horizontal scaling (adding more dedicated servers) can often be executed with a few clicks or an API call. This on-demand scalability is especially useful for businesses with seasonal workloads or those undergoing rapid growth, enabling them to avoid overprovisioning and reduce operational costs.
Security
Security is a core advantage of Cloud Dedicated Servers. They offer physical isolation from other tenants, ensuring that sensitive data and applications are not exposed to “noisy neighbor” risks commonly seen in public cloud environments. Providers often integrate enterprise-grade security features, such as dedicated firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), data encryption at rest and in transit, and multi-factor authentication (MFA). Compliance certifications—including ISO 27001, HIPAA, and PCI DSS—are typically available, making cloud dedicated servers suitable for industries with stringent regulatory requirements such as finance, healthcare, and e-commerce. Furthermore, security policies can be centrally managed and automated via orchestration tools, ensuring real-time compliance and rapid response to threats.
Typical Scenarios and Applications
Given their combination of performance, scalability, and security, Cloud Dedicated Servers are ideal for a wide range of use cases across various sectors:
– High-Traffic Web Applications: For e-commerce sites, SaaS platforms, and online media streaming services experiencing large volumes of concurrent users, dedicated resources ensure consistent uptime and optimal user experience.
– Database Hosting: Resource-intensive databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or NoSQL engines benefit from the high IOPS, RAM, and dedicated CPU, eliminating performance bottlenecks.
– Virtualization and Private Cloud: Organizations can deploy their own virtualization stacks (e.g., VMware, Hyper-V) to create private clouds, leveraging the control and isolation of dedicated hardware.
– Big Data and Analytics: Processing large datasets and running complex analytics workloads require consistent high-performance resources, which are provided by cloud dedicated servers.
– Disaster Recovery and Backup: Cloud dedicated servers can serve as hot or cold standby environments, offering rapid failover and robust data protection in case of primary site failures.
– Compliance-Driven Applications: Healthcare applications (HIPAA), financial services (PCI DSS), and government workloads benefit from the enhanced security, isolation, and auditability.
– Gaming Servers: Hosting multiplayer online games requires low-latency, high-performance infrastructure that can scale to accommodate spikes in user activity.
Cloud Dedicated Servers empower organizations to meet today’s demanding IT needs with uncompromising performance, elastic scalability, and enterprise-grade security. Their versatility makes them fit for a diverse range of applications, from robust web hosting to high-security transactional databases and analytics. By leveraging these servers, businesses can remain agile, secure, and competitive in an increasingly digital-first world.
Deployment and Management of Cloud Dedicated Servers
Provisioning
The deployment of Cloud Dedicated Servers leverages the automation and rapid provisioning capabilities of leading cloud platforms. Unlike traditional on-premises dedicated servers, which often require manual hardware setup, procurement, and extended lead times, cloud dedicated servers can be provisioned within minutes through intuitive web-based control panels or RESTful APIs. IT administrators can select the optimal hardware specifications—including CPU, RAM, storage type (HDD, SSD, NVMe), and network interfaces—directly from a cloud marketplace or provider dashboard. Advanced options may include selecting the geographic data center location for latency optimization or regulatory compliance. Once selected, the server image is instantiated, and the operating system—whether Linux, Windows Server, or custom images—is automatically deployed, bringing the server online and ready for configuration.
Configuration
Once provisioned, initial configuration is critical to ensure that the Cloud Dedicated Server is secure, optimized, and tailored to the organization’s requirements. Configuration tasks typically include:
– Operating System Hardening: Applying security patches, disabling unused services, configuring firewalls, and setting user permissions.
– Network Configuration: Assigning public and private IP addresses, configuring VLANs, and integrating with Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) for network segmentation.
– Storage Management: Setting up RAID arrays, encrypting volumes, and mounting network-attached storage (NAS) or block storage as required.
– Resource Allocation: Fine-tuning system resources for specific workloads, such as allocating more memory to database servers or optimizing CPU scheduling for application servers.
– Automation Scripts: Utilizing configuration management tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef to automate repetitive setup tasks and enforce consistency across multiple deployments.
Additionally, cloud providers often offer ready-to-use images with pre-installed software stacks, containerization support (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes), and integration with DevOps pipelines to streamline application deployment.
Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is an essential component of Cloud Dedicated Server management, ensuring high availability, performance, and security. Modern cloud ecosystems provide a comprehensive suite of monitoring tools and dashboards that deliver real-time insights, including:
– Performance Metrics: CPU, memory, disk I/O, and network usage are tracked to detect resource bottlenecks and forecast scaling needs.
– Application Monitoring: Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tools provide end-to-end visibility into the health and responsiveness of software running on the server.
– Security Monitoring: Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), log analysis, and audit trails help identify and mitigate unauthorized access or suspicious activity.
– Automated Alerts: Threshold-based alerting notifies administrators of issues such as high CPU utilization, storage nearing capacity, or failed backups, enabling proactive intervention.
For organizations with compliance requirements, monitoring systems often support audit logging and centralized log aggregation, making it easier to meet regulatory reporting standards.
Best Practices
To realize the full benefits and maintain the reliability of Cloud Dedicated Servers, organizations should adhere to industry best practices throughout the server’s lifecycle:
– Automate Where Possible: Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to automate provisioning, configuration, and scaling, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency.
– Implement Robust Security Measures: Conduct regular security audits, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA), enforce least-privilege access, and keep systems up to date with the latest patches.
– Backup and Disaster Recovery: Set up automated, scheduled backups and test restoration procedures frequently to ensure business continuity in case of system failures.
– Resource Optimization: Regularly review server usage to identify underutilized resources, right-size instances, and implement auto-scaling policies.
– Documentation and Change Management: Maintain thorough documentation of configuration changes, access rights, and system updates to support troubleshooting and compliance.
– Monitor and Respond: Set up comprehensive monitoring and incident response protocols to quickly address emerging issues and optimize long-term performance.
The deployment and management of Cloud Dedicated Servers are streamlined by automation, advanced monitoring, and best practices that enable organizations to maintain high-performing, secure, and resilient IT infrastructure. By leveraging the dynamic capabilities of the cloud, IT teams can provision resources rapidly, configure environments with precision, and monitor workloads at scale, all while enforcing strong security and compliance standards. These practices position organizations to maximize uptime, minimize risk, and accelerate digital transformation initiatives with confidence.
Conclusion
Cloud Dedicated Servers are redefining the foundation of modern IT infrastructure, bridging the gap between traditional dedicated servers and cloud flexibility. By offering isolated physical resources, enhanced security controls, and seamless scalability, these servers are ideal for handling demanding enterprise workloads such as e-commerce platforms, financial applications, and data-intensive analytics. Their ability to be rapidly provisioned and managed through intuitive cloud platforms reduces operational overhead while delivering consistent uptime and compliance with industry standards. The deployment and management of cloud dedicated servers emphasize best practices such as proactive monitoring, automated backups, and regular security audits, ensuring business continuity and data integrity. As organizations continue to adapt to digital transformation and evolving security threats, adopting cloud dedicated servers enables them to future-proof their IT environments. Investing in this technology supports robust performance, operational agility, and a secure foundation for innovation—making it a strategic choice for businesses aiming to stay competitive in a dynamic market.
Keywords:
- SEMTEK Cloud server
- Cheap dedicated server
- Contabo dedicated server
- Interserver dedicated server
- Ovh server
- Asia server
- Dedicated server hetzner
- VPS server Minecraft
- Leaseweb
Source:
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt