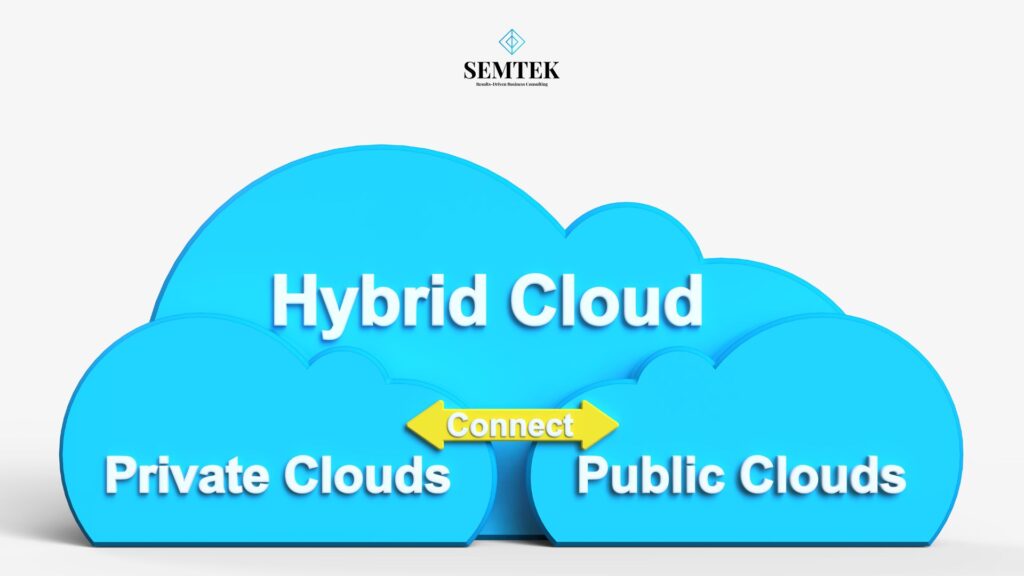
The hybrid cloud model exists as an advanced IT infrastructure system which combines private cloud resources with public cloud services. Organizations choose the hybrid cloud because it delivers flexible data management and deployment options which enable their search for agile scalable cost-effective solutions. Organizations achieve better resource management through the integration of their on-premises data centers with public cloud services from AWS and Azure and Google Cloud. Organizations can protect their sensitive data by running it in a private cloud yet use public cloud resources for non-sensitive operations. The model provides a flexible framework which supports modern business requirements through its ability to promote innovation and growth while maintaining strong security standards and regulatory compliance.
Definition and Components of Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud Overview
The hybrid cloud system unites private clouds which operate on-premises with public cloud services to create an innovative solution. The integration enables businesses to exchange data and applications between these environments which leads to improved operational flexibility and deployment alternatives. Organizations can access improved resource management by running their operations between private and public cloud platforms.
Core Components
– Private Cloud:
Private clouds function through dedicated computing systems which serve only one organization. Organizations can find these resources either on-site or in their own data center or they can choose third-party hosting services that remain dedicated to their organization. This component provides enhanced data control and security measures which makes it suitable for handling sensitive information and essential business operations.
– Public Cloud:
Third-party service providers operate public clouds through platforms which include Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform. The environments consist of shared resources which different organizations can access. Businesses gain two main advantages from public clouds which let them scale up their operations and remain adaptable while avoiding the need to purchase extra equipment.
– Hybrid Connectivity:
The component enables secure network connections which allow data and application integration between private and public cloud environments. The system allows users to transfer data securely and efficiently through hybrid connections which link separate cloud environments. The connectivity functions as a core necessity which enables hybrid cloud deployment to reach its complete operational capacity.
The hybrid cloud system unites private and public cloud benefits to create a flexible computing platform which delivers optimal performance. Organizations can use this system to handle their IT assets through strategic planning which unites cost management with performance optimization and security measures that match their specific requirements.
Benefits and Challenges of Hybrid Cloud
Benefits
– Scalability:
Organizations get unmatched scalability through hybrid cloud systems which let them manage their work between private and public cloud resources. Businesses can adjust their operational scale through expansion or reduction without needing to invest in major financial resources. The system provides operational flexibility which enables businesses to manage high workloads effectively while keeping standard performance levels intact.
– Cost Efficiency:
Organizations get cost optimization through their use of private and public clouds together. Private clouds safeguard sensitive information and essential operations because they provide complete control yet public clouds serve cost-effective solutions for handling less critical operations. The organization maintains a balance between cost control and data security to protect important information.
– Agility and Flexibility:
Organizations get the ability to modify their market approach and business processes through the hybrid cloud model. Organizations can deploy new applications and services rapidly, fostering innovation and allowing them to respond to competitive pressures without the constraints of traditional infrastructure limitations.
– Security and Compliance:
Private environments within hybrid clouds enable organizations to secure essential workloads which brings improved security and compliance advantages. Organizations maintain strict data control which enables them to obey regulations and protect against security incidents.
Challenges
– Complex Management:
Organizations need to implement advanced management systems and tools because hybrid cloud environments consist of multiple distributed resources which require complex management. The system needs proper monitoring tools together with trained personnel who understand how to operate between different cloud platforms.
– Integration Issues:
A hybrid cloud system requires organizations to achieve integration capabilities which function at a high level. Organizations need to deploy powerful APIs together with middleware systems which enable smooth data transfer between different cloud environments to maintain operational flow and system performance.
– Data Transfer and Latency:
Hybrid cloud systems encounter major difficulties when they need to handle data movement and delay issues. The process of transferring large data volumes between private and public cloud systems creates problems because it can lead to delayed data accessibility. Organizations need to establish data management systems which reduce delay times while making information accessible at its required time and location.
The hybrid cloud system provides multiple advantages through its scalable architecture and cost-effective solutions and secure framework yet organizations face difficulties when they manage it and connect its components and transfer data between systems. Organizations need to evaluate these factors when they decide to implement a hybrid cloud strategy because this evaluation will help them use the model effectively while addressing its potential drawbacks.
Use Cases and Industry Applications of Hybrid Cloud
Enterprise IT
The enterprise IT sector depends on hybrid cloud solutions because organizations need these solutions to support their existing on-premises infrastructure investments. Organizations face difficulties when they try to transform their IT systems because these changes often disrupt their current operational processes. The organizations should select hybrid cloud systems to migrate their operations toward public cloud scalability through public cloud resources while preserving their essential functions within private cloud environments. The method enables organizations to use their resources at their best while they move from one system to another in different stages which protects business operations from disruptions.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry depends on hybrid cloud solutions because they protect sensitive patient information through secure storage and provide access to modern analytical tools. The healthcare providers need to safeguard patient information through proper storage and processing because HIPAA and other data protection laws require it. Healthcare organizations protect sensitive patient information through private clouds which meet security standards but they use public clouds to run analytical operations and make decisions. The combination of these technologies delivers better patient care alongside operational efficiency while safeguarding all patient information privacy.
E-commerce
The e-commerce sector uses hybrid clouds to separate operations between private clouds which handle secure transactions and public clouds which manage customer information and analytical processes. E-commerce platforms need to handle large volumes of customer information together with transactional data through secure and efficient methods. Organizations can protect transactional data by using hybrid cloud systems which operate in secure environments yet public cloud resources handle scalable customer data analytics. The system provides improved customer service and operational efficiency and protects financial transactions from security risks.
Software Development
The hybrid cloud environment provides software developers with a secure platform that enables them to perform their development work and run their tests. Developers need environments which they can quickly create and expand to fulfill their various development and testing requirements. The hybrid cloud system enables developers to run their applications in a protected private cloud environment while they can also use public clouds for testing at scale and deployment purposes. The method speeds up the development process while supporting continuous integration and deployment and allowing developers to create new features at a rapid pace without sacrificing security or system stability.
The hybrid cloud solutions provide flexible options which organizations can customize to meet their specific industry requirements. Hybrid clouds deliver flexible secure solutions at affordable costs which organizations can use to manage IT workloads and protect healthcare data and optimize e-commerce operations and accelerate software development processes.
Conclusion
Organizations that adopt a hybrid cloud strategy get to combine private cloud security with public cloud scalability and innovation potential. The hybrid cloud system provides multiple advantages to users although it presents complex operational challenges which include cost savings and improved flexibility and better resource management. Organizations achieve better data transfer operations through advanced management tools which work together with powerful APIs to solve integration problems. The hybrid cloud platform operates across multiple sectors which include healthcare and e-commerce and software development to support various business requirements that enhance operational efficiency and drive innovation. Businesses rely on the hybrid cloud as their main IT structure because it enables them to handle changing market needs and technological progress effectively.
Keywords:
- Hybrid cloud example
- Hybrid cloud vs multi cloud
- Hybrid cloud storage
- Hybrid cloud types
- Hybrid cloud architecture
- Hybrid cloud example in real life
- Advantages of hybrid cloud
- Hybrid cloud AWS
Related:
Sources:
1. Definition and Components
Zissis, D., & Lekkas, D. (2014). Cloud computing basics. In Cloud Security (pp. 1–25). Springer. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/978-1-4302-6146-9_1.pdf
> This source provides foundational definitions of cloud computing based on the NIST framework, detailing service and deployment models including hybrid cloud, and explains the technological evolution leading to hybrid architectures.
2. Benefits and Challenges
Hasimi, L., & Penzel, D. (2023). A case study on cloud computing: Challenges, opportunities, and potentials. In Developments in Information and Knowledge Management Systems for Business Applications (pp. 1–25). Springer. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-27506-7_1
> This chapter explores hybrid cloud adoption from the customer’s perspective, highlighting cost efficiency, scalability, and compliance benefits, while also addressing integration, governance, and security challenges.
3. Use Cases and Industry Applications
Zong, K., & Zhang, J. (2025). A novelty method for solving the multi-objective problem of industrial internet of things service placement in fog computing. Cluster Computing, 28, Article 812. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10586-025-05455-1
> This article discusses hybrid cloud and fog computing applications in industrial IoT, emphasizing latency-sensitive use cases in sectors like robotics, oil and gas, and automotive, and proposes reinforcement learning-based optimization strategies.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt